Introduction: Why Understanding the Wi-Fi Extender vs Booster Difference Matters
In our hyper-connected world, slow internet is more than just a frustration—it’s a dealbreaker. Whether you’re working from home, streaming your favorite series, or gaming online, a reliable Wi-Fi signal is essential. But when your router can’t reach every corner of your space, you might find yourself wondering: Should I get a Wi-Fi extender or a Wi-Fi booster?
The terms are often used interchangeably, but they don’t mean exactly the same thing. Understanding the wifi extender vs booster difference can save you money, boost your network performance, and eliminate dead zones for good.
What Is a Wi-Fi Extender?
A Wi-Fi extender, sometimes called a “range extender,” works by capturing your existing Wi-Fi signal and rebroadcasting it to areas with weak coverage. Think of it as a middleman that bridges the gap between your router and your devices.
How a Wi-Fi Extender Works
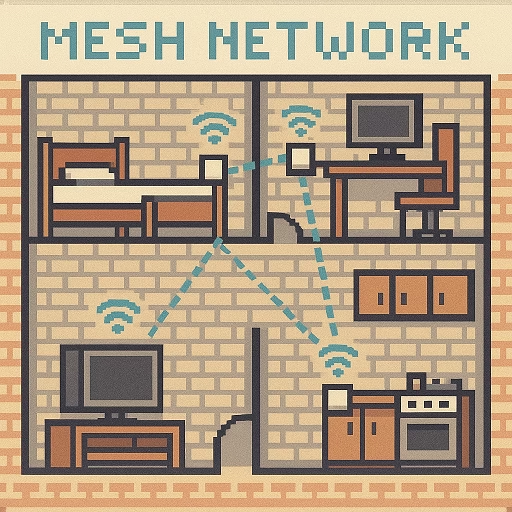
When placed midway between your router and the dead zone, an extender connects wirelessly or via Ethernet to your router. It then retransmits that signal, extending coverage but sometimes with a minor delay or speed reduction.
Pros and Cons of Using a Wi-Fi Extender
Pros:
- Affordable and easy to install
- Great for eliminating weak spots
- Works with most standard routers
Cons:
- Can reduce overall bandwidth
- May require manual switching between networks (e.g., “HomeWiFi” vs “HomeWiFi_EXT”)
- Signal can weaken if placed too far from the router
What Is a Wi-Fi Booster?
While similar in concept, a Wi-Fi booster is a broader term that includes both extenders and amplifiers. Its goal is to enhance your signal strength and speed, especially when your Wi-Fi is unstable or limited by interference.
How a Wi-Fi Booster Enhances Your Signal
Boosters can work in different ways—some amplify the signal from your router, while others improve its power output. Certain advanced boosters even integrate mesh networking features for seamless roaming.
Key Advantages and Disadvantages of a Wi-Fi Booster
Advantages:
- Increases signal strength and coverage
- Compatible with multiple devices
- Some models include Ethernet ports for wired stability
Disadvantages:
- Slightly more expensive than extenders
- Setup can be more complex
- May cause network interference if poorly positioned
Wi-Fi Extender vs Booster: Side-by-Side Comparison
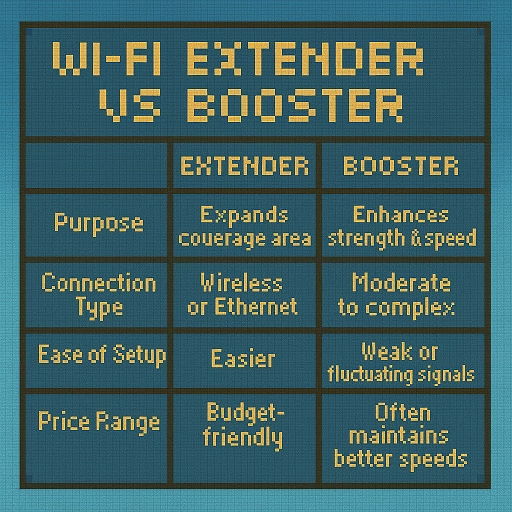
| Feature | Wi-Fi Extender | Wi-Fi Booster |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Expands coverage area | Enhances strength & speed |
| Connection Type | Wireless or Ethernet | Wireless, Ethernet, or mesh |
| Ease of Setup | Easier | Moderate to complex |
| Ideal Use Case | Dead zones | Weak or fluctuating signals |
| Price Range | Budget-friendly | Mid to high-end |
| Speed Impact | Can reduce bandwidth slightly | Often maintains better speeds |
Common Misconceptions About Wi-Fi Extenders and Boosters
Many users assume extenders and boosters are identical, but that’s not entirely true. Another common myth is that an extender will double your speed — it won’t. Instead, it expands reach. Similarly, boosters don’t always mean higher Mbps; they enhance stability and reduce lag.
Which One Should You Choose? (Extender vs Booster)
For Large Homes
Opt for a booster or mesh Wi-Fi system. They provide consistent coverage across multiple floors and walls.
For Apartments or Small Spaces
A Wi-Fi extender is often sufficient. It’s budget-friendly and quick to install.
For Businesses or Offices
Choose a Wi-Fi booster with dual-band support and Ethernet ports to ensure stable connections for multiple users.
Best Practices for Maximizing Wi-Fi Coverage
Placement Tips for Better Signal Strength
- Keep your extender or booster halfway between your router and the weak zone
- Avoid placing it near metal surfaces or microwaves
- Elevate it slightly for better signal distribution
Using Mesh Systems as an Alternative
Mesh networks are a modern upgrade combining the best of both worlds. They use multiple nodes to ensure seamless connectivity without switching networks.
Real-World Examples and User Experiences

Users often report that extenders are perfect for filling in weak zones like garages or balconies, while boosters excel at stabilizing signals for gaming or video conferencing. In one case, upgrading from an extender to a booster improved Wi-Fi speeds by nearly 40%.
FAQs About Wi-Fi Extenders and Boosters
Q1. Are Wi-Fi extenders and boosters the same thing?
Not exactly — extenders expand range, while boosters enhance signal power.
Q2. Do Wi-Fi boosters increase internet speed?
They improve signal strength and stability, but your maximum speed still depends on your internet plan.
Q3. Can I use an extender and booster together?
Yes, though it’s best to ensure they’re compatible to avoid interference.
Q4. How far can a Wi-Fi extender reach?
Most extenders can add 50–150 feet of additional coverage.
Q5. Do mesh systems replace boosters?
In many ways, yes. Mesh systems offer broader, more seamless coverage.
Q6. Which is better for gaming — an extender or booster?
A booster, preferably one with an Ethernet connection, offers lower latency for gaming.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Connectivity Needs
When it comes to the wifi extender vs booster difference, your choice depends on your unique setup. If you simply need to fill in weak spots, go for an extender. But if your goal is stronger, faster, and more stable Wi-Fi throughout your space, a booster (or even a mesh system) may be worth the upgrade.
No matter your choice, smart placement and quality hardware will always make a noticeable difference in your Wi-Fi experience.
(External Link: Learn more about optimizing your network from How-To Geek.)
